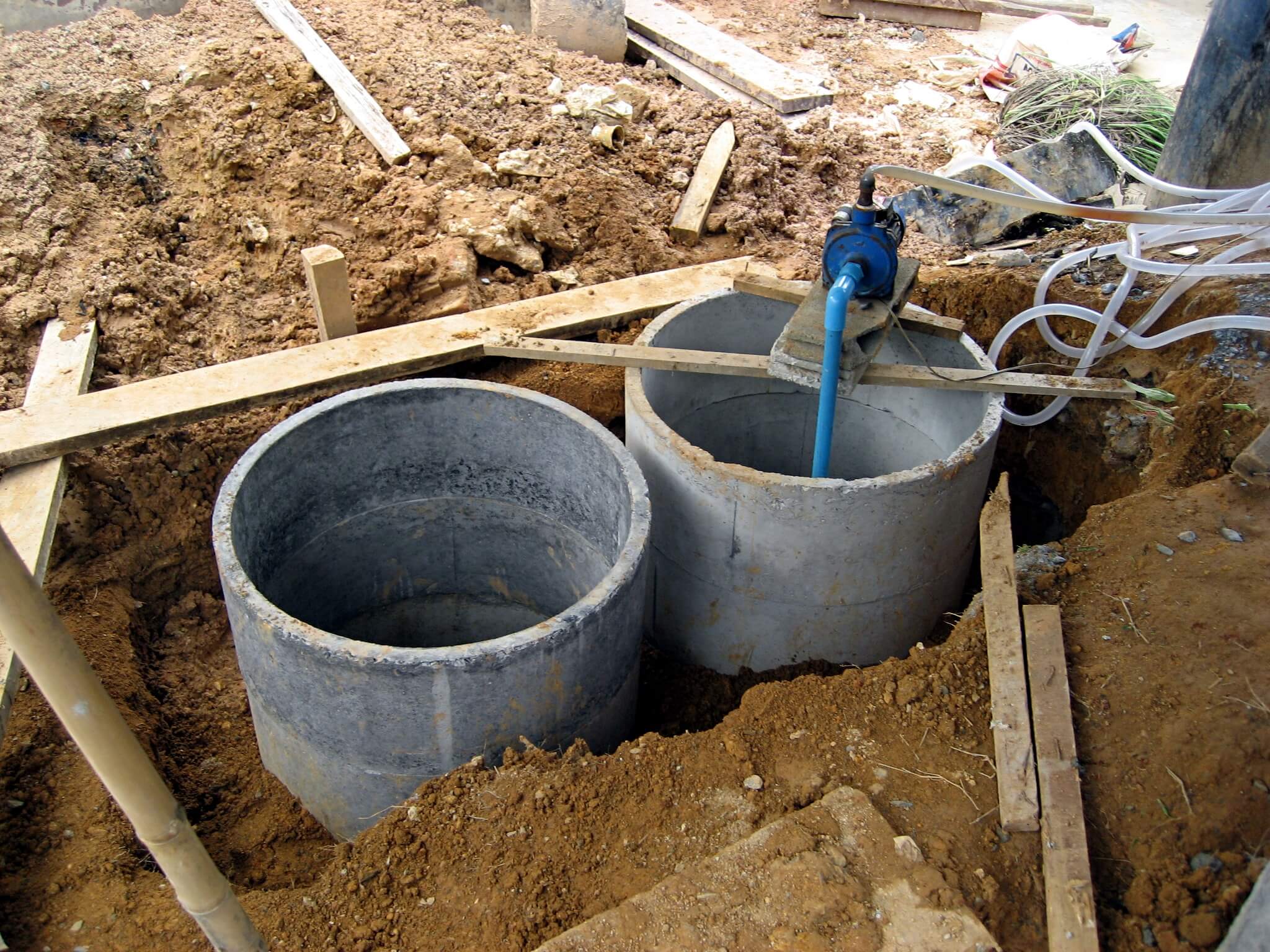
Septic systems are underground tanks made of compartments installed in domestic and commercial estates. It collects water waste and fecal waste from cisterns and toilets.
Khaosaming, CC BY-SA 3.0 https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0, via Wikimedia Commons
Then they are decomposed by anaerobic bacteria. Standard septic should have at least 2 to 3 layers or chambers. When properly maintained, a septic tank can last up to 20 to 40 years or more. This is why it is important to find the right professional to consult with.
How Septic Systems Work:
1. The wastewater and fecal wastes from toilets and kitchen run through a pipe and into the septic tank, which has three layers:
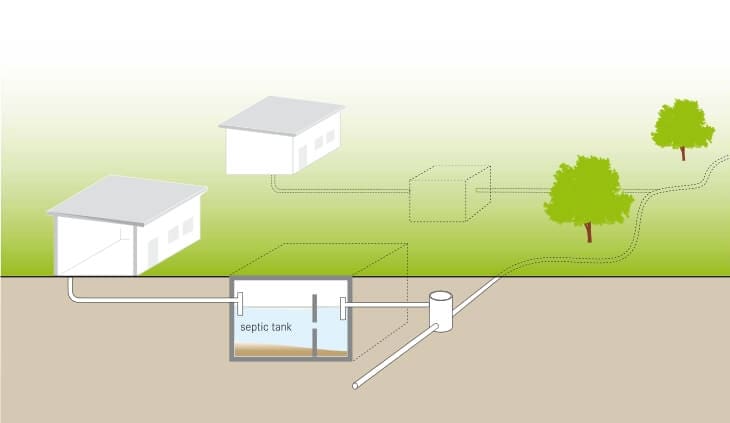
- First layer/Scum Layer: Composed of grease, oil, and other fluids or floatable.
- Second Layer: Consists of particles and fluid.
- Third Layer: Consists of layers of sludge and other heavier components.
2. Next, the liquid is discharged into the drain field through the pipes or pumped out from the tanks.
3. For inspection purposes, maintenance holes are installed. It allows the professionals to be able to pump the wastes from the tanks when full.
4. Gas accumulates over time inside the tank, which may blow up the tank when it is not dispersed in the open. For this reason, pipe vents are installed at least 2 meters in height.
Types of Septic Tank Structure:
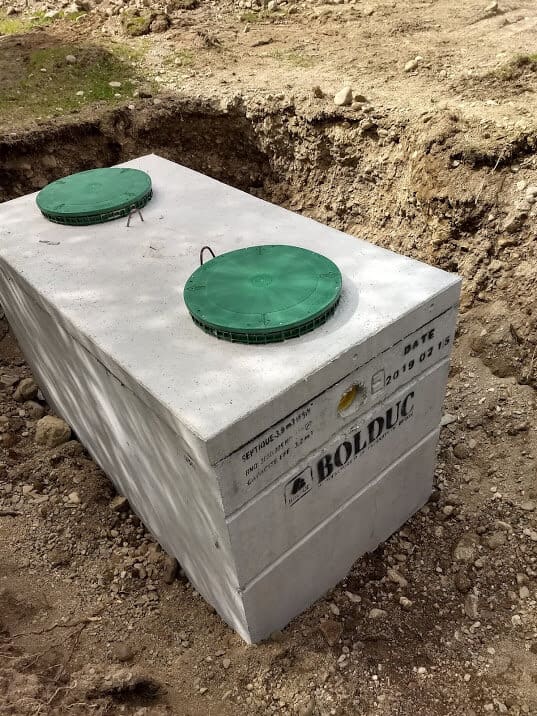
1. Concrete

Benefits: A concrete septic tank is the most used and preferred due to its longevity. It is watertight and durable enough to prevent leaks. Furthermore, it has a high effluent capacity compared to its counterparts, and they are likely to decompose over time, minimizing the need to keep pumping the wastes inside.
Disadvantages:
- They are easily corroded.
- Easily penetrated by the roots of trees.
- Cracks in extreme hot and cold weather conditions.
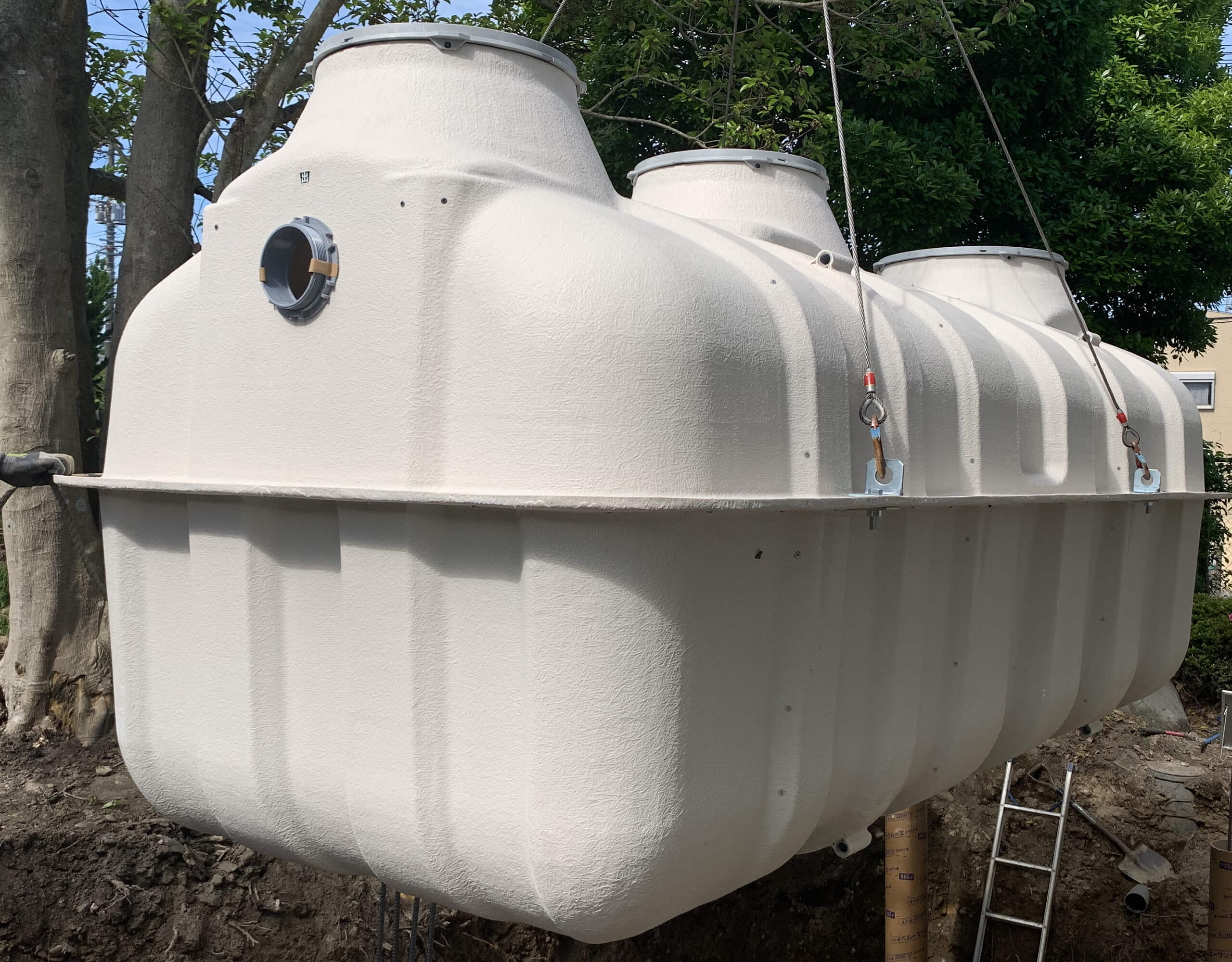
2. Fiberglass
Fiberglass is made of fiber or thick modified plastic. It has two main outlets. The inlet is responsible for collecting water while the outlet removes the pre-processed wastewater and distributes them either on the soil and water source.
Benefits:
- This type can also last up to 30 years if properly installed.
- They are easy to install, sturdy, budget-friendly, and durable.
Disadvantage:
- It can be hard to detect damage on the material until it is used and full.
3. Plastic
Plastic septic systems are lightweight, which makes them easier to install.
Benefits:
- They are cheap.
- It is easier to install.
- They are resistant to corrosion and cracks.
- Hygienic
- Flexible
- Rust-resistant
Disadvantages:
- It can be deformed in hot weather conditions.
- Easily crushed.
- Requires higher maintenance.
4. Steel
Steel septic tanks only last up to 25 years as they are prone to rust. It is for this reason that makes it the least option.
Benefits:
- Durable
Disadvantages:
- Susceptible to rust. When the covers rust, it becomes too weak to withhold the pressure or weight put on it. It puts any person or animal the risk of falling into the tank.
- Needs constant replacement and monitoring.
Types of septic tank systems:
1. Conventional Septic Tank
The conventional septic tank is the simplest form of a septic system. It is divided into two components which are the septic tank and the drain field. The drain field system is installed underground and is responsible for the exit of the effluents. It consists of gravel-filled trenches and plastic pipes through which the waste passes through and into the soil. This is the least expensive choice but needs constant maintenance and pumped every 2 to 3 years.
The advantages of using this type are its low maintenance and low-cost operation. On the other hand, it gives lower affluence and is not recommended in sensitive areas such as clay soils, shallow soils, and rocky soils.
2. Chamber System
The Chamber system is an example of a gravelless drain field. A gravelless system does not use gravel in its drain field beds or trenches. Instead, it uses sand fiber membrane, rubber, plastic, glass, clay, and shale. These materials are recycled into pipes.
The Chamber system consists of connected chambers and pipes, which collect wastewater from the residential homes into the septic tanks and eventually to the drain field or chambers to contact the soil. The microbes on the earth will then treat the effluent.

3. Aerobic Treatment Unit
The aerobic treatment unit pumps oxygen into the tank allowing the growth of aerobic bacteria, which is responsible for the breakdown of the effluent. This design is primarily used in residential homes with fewer spaces and homes near water sources sensitive to contamination. Aerobic treatment is divided into three components:
A. The trash tank takes the initial step of collecting wastewater and allowing it to separate into three layers, the scum layer on top, the liquid effluent in the middle, and the bottom layer called sludge.
Then, the liquid effluent flows to the aerobic treatment unit.
B. The aerobic treatment unit uses oxygen to process the effluent and break down the harmful pathogens in the liquid effluent. The process of pumping air requires a mechanical and electrical operation.
C. The next step is disinfection. This involves chlorine, UV irradiation, bleach, and other disinfectants to treat the effluent before it is released to the pump tank.
You can have your aerobic septic system installed in high water table zones and where conventional methods cannot. It can also produce high-quality effluent. However, if this is not vented or maintained correctly, it could disperse nasty smell and contamination. Hence, regular maintenance is required to keep it in good condition, increasing costly operations. Frequent pumping is also needed.
4. Evapotranspiration System
An evapotranspiration septic system uses evaporation to dispose of wastewater. This is a good choice if you live in a sunny region. It uses three different methods. The first one uses a pretreatment method either a septic tank or an aerobic system to remove the particles and floatable solids before it is processed into vapor. It includes the use of sand, surface cover, and monitoring wells. Lastly, to enhance the transpiration process, vegetation is planted on the surface.
The second one uses the percolation method, which involves filtering the solids from the water before it is vented into the air. The third method uses mechanical procedures although this is still under development and is yet to be launched.
5. Cluster/Community System
This septic system offers a decentralized wastewater treatment from multiple users with pipes connected into a single septic tank and drain field. It is a cost-effective, efficient, and effective method that helps preserve open spaces. Furthermore, you can build this type quicker and easier. Community septic systems also provide a cheaper, safer, and more reliable waste treatment. Additionally, community septic systems are often installed in subdivisions and other rural areas with clustered communities.
6. Recirculating Sand Filter Septic System
Recirculating sand filter septic systems can either be installed above or underground. The process involves collecting wastewater from the residential homes to the septic tank, where it is broken down into scum layer, liquid effluent layer, and sludge layer. Next, it flows to the pump tank and is released into the sand filters. Sand filters are great for removing contaminants from the wastewater through chemical and biological processes. This process also eliminates the odor emitted by wastewaters.
It is commonly used in schools, subdivisions, mobile home parks, and small municipalities. This design is suitable in areas with minimal availability of soil for treatment and sites with shallow soil cover, high groundwater, and limited land area.
Things to consider before installing a septic tank:
1. Hire the right professionals
Hiring the right professionals to install your septic tank will increase the chance of securing its durability and longevity. It will minimize the risk of damaging your materials, wasting your time and money. Consider reviewing the following before trusting a company or contractor:
- Company license, insurance, and bonding
- Contractor’s license, skills, experience, and knowledge
- Company’s customer service
- Fees and hidden charges
- Website reviews and recommendations
Also, if you need a septic service, just go to Google and type “septic tank cleaning services near me” then you will find them.
2. Inspect
Once you find the right people to work on your septic system, have them inspect the area you plan on installing it. Make sure to list down necessary queries to make sure they do it right and provide you with insights. The inspection will determine the materials needed and the type of septic system suitable in your area, considering space, size, soil type, and so on. It will also provide you with an accurate estimate on how much you will be spending for the construction, labor along with the number of days the procedure will take.

3. Choose the right septic system
Choosing the proper septic should be based on the soil type, weather conditions, and price. Ask your contractor about his recommendations after the inspection. They may provide you with suitable options but make sure to choose something durable, low maintenance, and can last up to the standard 20 to 40 years regardless of the price.
4. Educate yourself on how to maintain your septic system
Educating yourself on the basics of septic systems will help you understand how they work. This will provide you with knowledge on the dos and don’ts. Proper maintenance will not only prevent your tank from early destruction but will also help you detect possible problems such as cracks, rusts, and others. Lastly, be sure to be present during the installation process.







